Close
Safety in warehouse
Safety in warehouse
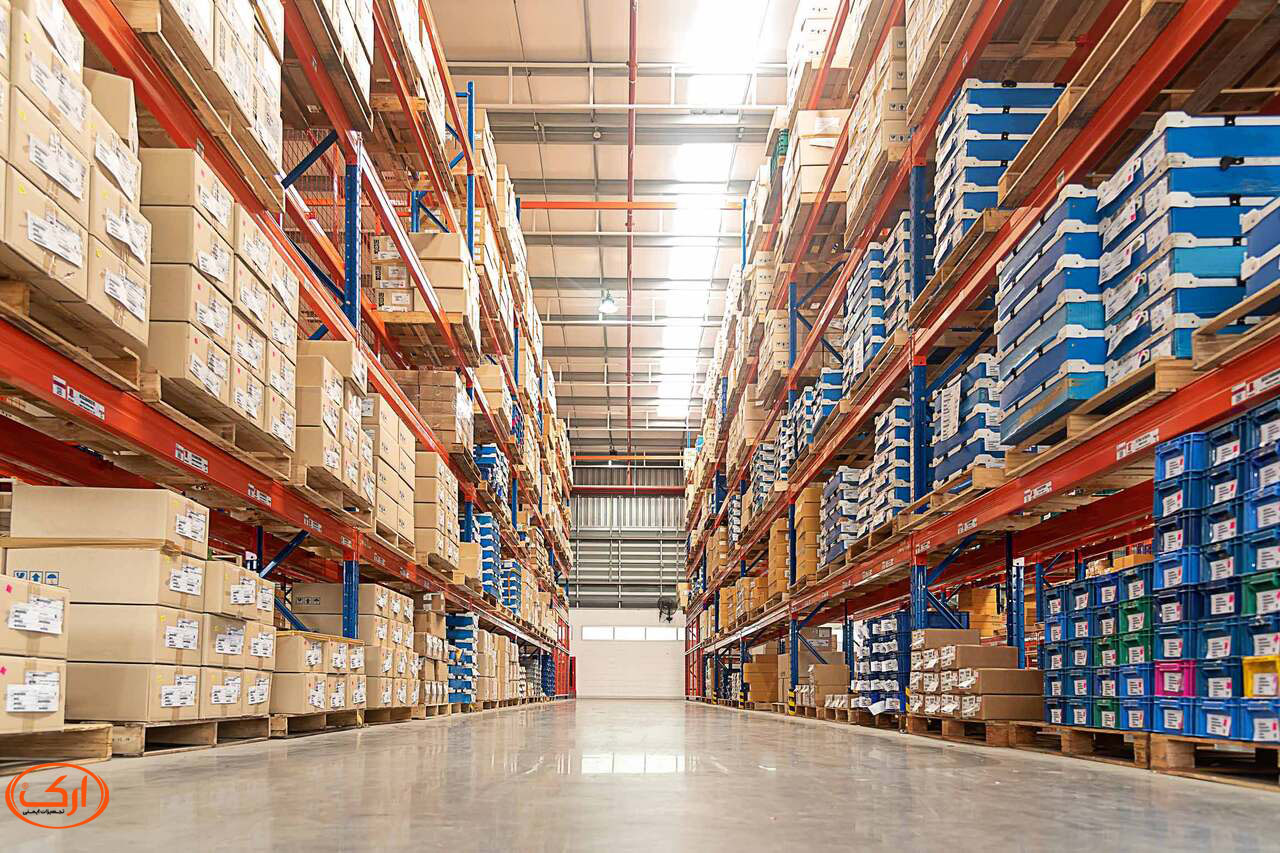
Warehouse Safety consists of regulatory guidelines that result in having a safe workplace and increasing safe action when doing tasks in the storehouse, therefore, causing warehousing personnel to encounter low risk.
According to the reported statistics by the U. S Bureau of Labor Statistics, an average of 16 people annually lose their lives in the warehouse and storage sector in the United States, and the injury and illness rate is 5 out of every 100 warehouse workers. Therefore, it is essential to be potential hazards in the warehouse.
Forklift safety
A forklift is a fundamental piece of equipment used in the warehouse. Occupational Safety and Health Administration(OSHA) reported unsafe use of forklifts is a common hazard in the storehouse. Hazardous use of forklifts can cause damage to the operator, adjacent workers, and property surrounding it.
Some important points when using a forklift is:
• Forklift operators have to be qualified and trained; if operators lack certification, operators will be trained and evaluated
• Daily inspection of forklift equipment

Safety of docks and risk control
When a forklift leaves the docks and hits someone leads to stuck or crushed organs between a forklift and a dock. In this condition the operator should do below for safety of personal:
• The operator should drive the forklift slowly on the dock`s pallet and also make sure the dock edges are resistant and safe for bearing loads.
• Using signs and warning devices to prevent personnel from approaching the docks.
Safety of conveyor belt and risk control
Conveyor belts transport objects or materials from one warehouse to another. The conveyor belt’s hazards include getting stuck between the equipment and colliding with falling objects. Following the points below can enhance the safety of the warehouse:
• Use appropriate protective equipment between the conveyor belt and the worker to protect them against the entangling of clothes, organs, and hair.
• Take advantage of suitable locks, during repair and maintenance.
The basic layout of materials (proper arrangement of materials)
Improperly arranging loads and inappropriately maintaining the material in the box lead to slipping and creating unintended hazards. The aisle and passageways should be in good condition to prevent the slipping of workers. Ensure that loads are placed uniformly and correctly. Stacking heavier loads on lower or middle shelves is important and always remember to lift one of the loads each time.
Manual lifting and handling
Improper manual lifting and handling are common reasons for physical injuries in warehouses. Musculoskeletal disorders will occur if a worker does not follow an appropriate approach. Especially when done with improper postures, repetitive movements, or excessive strain, it can exacerbate musculoskeletal disorders. Adhering to the point below can decrease the possibility of musculoskeletal disorders:
• Observing a suitable ergonomic position during lifting and handling loads. Receiving assistance when the load is heavy.
• Personnel should train more about the principles of ergonomics in the workplace.
• Before anything, consider using a lift instead of manual carrying.

Safety of hazardous chemicals
Safety risk communication must be implemented during work with hazardous chemicals. Safety risk communication share information associated with the hazards and safety solutions for dangerous chemicals (Proper storage and disposal of chemicals and use of appropriate PPE (Personal Protective Equipment)).
Knowing how to conduct safety inspections and properly handle and store chemicals is critical for both workers and management teams to ensure the warehouse is safe.
Safety of forklift charging stations
Charging stations located in the warehouse is used to charge electrical equipment. Also gasoline or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) may used.
Failure to follow warehouse safety instructions may result in fire and explosion. Some safty tips is:
• Design charging stations to be located away from open flames.
• Smoking is forbidden.
• Use appropriate Personal Protective Equipment(PPE).
• Fire extinguishers must be placed at a suitable distance.
• Charging stations should include proper ventilation to control harmful gases.
• If workers are exposed to acids and chemicals, they should have access to eyewash and shower facilities.
Controlling hazards related to high-energy equipment
Implementing a Lockout/Tag out (LOTO) program in all warehouse operations is necessary to ensure that all energized equipment is properly shut down and prevent personnel from becoming trapped between mechanical parts or electrocuted. All workers affected by this program must receive training in LOTO procedures and how to apply and remove LOTO devices after repairs are
made to ensure the warehouse`s safety.
made to ensure the warehouse`s safety.

 Military Shoe
Military Shoe
 Safety Shoe
Safety Shoe
 Work Wear
Work Wear
 Office Shoe
Office Shoe
 Hiking Shoe
Hiking Shoe